How nodes work
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes
Docker Engine 1.12 introduces swarm mode that enables you to create a cluster of one or more Docker Engines called a swarm. A swarm consists of one or more nodes: physical or virtual machines running Docker Engine 1.12 or later in swarm mode.
There are two types of nodes: managers and workers.
If you haven’t already, read through the swarm mode overview and key concepts.
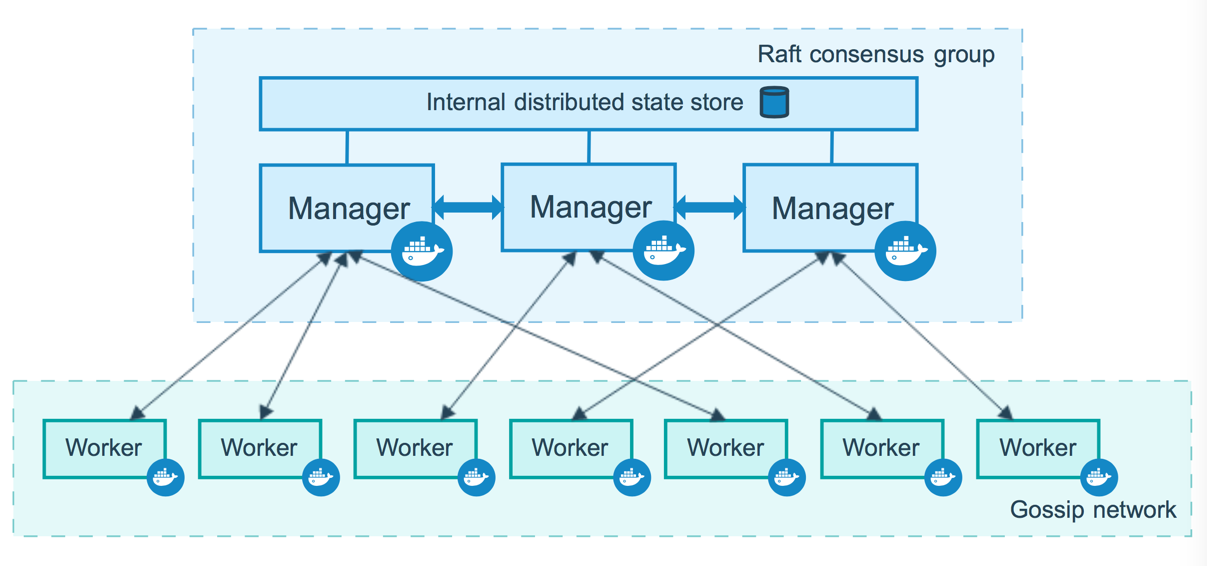
Manager nodes
Manager nodes handle cluster management tasks:
- maintaining cluster state
- scheduling services
- serving swarm mode HTTP API endpoints
Using a Raft implementation, the managers maintain a consistent internal state of the entire swarm and all the services running on it. For testing purposes it is OK to run a swarm with a single manager. If the manager in a single-manager swarm fails, your services continue to run, but you need to create a new cluster to recover.
To take advantage of swarm mode’s fault-tolerance features, Docker recommends you implement an odd number of nodes according to your organization’s high-availability requirements. When you have multiple managers you can recover from the failure of a manager node without downtime.
- A three-manager swarm tolerates a maximum loss of one manager.
- A five-manager swarm tolerates a maximum simultaneous loss of two manager nodes.
- An
Nmanager cluster tolerates the loss of at most(N-1)/2managers. -
Docker recommends a maximum of seven manager nodes for a swarm.
Important Note: Adding more managers does NOT mean increased scalability or higher performance. In general, the opposite is true.
Worker nodes
Worker nodes are also instances of Docker Engine whose sole purpose is to execute containers. Worker nodes don’t participate in the Raft distributed state, make scheduling decisions, or serve the swarm mode HTTP API.
You can create a swarm of one manager node, but you cannot have a worker node
without at least one manager node. By default, all managers are also workers.
In a single manager node cluster, you can run commands like docker service
create and the scheduler places all tasks on the local Engine.
To prevent the scheduler from placing tasks on a manager node in a multi-node
swarm, set the availability for the manager node to Drain. The scheduler
gracefully stops tasks on nodes in Drain mode and schedules the tasks on an
Active node. The scheduler does not assign new tasks to nodes with Drain
availability.
Refer to the docker node update
command line reference to see how to change node availability.
Change roles
You can promote a worker node to be a manager by running docker node promote.
For example, you may want to promote a worker node when you
take a manager node offline for maintenance. See node promote.
You can also demote a manager node to a worker node. See node demote.